New report highlights how pharmacy can redefine role within NHS

The National Pharmacy Association (NPA) has published a new report outlining how independent pharmacies are ready to redefine their role within the NHS.
The NPA has published a medium-term prospectus for the development of pharmacy services, calling it a challenge to old ways of thinking and an opportunity to redefine the sector’s role in the NHS.
It follows months of dialogue with NPA members about what a clinical future could look like for the sector.
The document, Making Changes, Meeting Needs, will be shared with the King’s Fund and Nuffield Trust who are currently working on a new vision for the future on behalf of Community Pharmacy England.
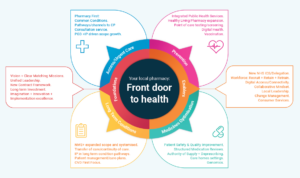
Among the ambitions in the NPA’s prospectus are:
- Improve the management of long-term conditions such as asthma, hypertension, heart failure and diabetes.
- Expand preventative interventions to help make the NHS a wellness, health-inequality reversing service.
- Shift focus from a downstream dispensing role to an end-to-end prescription management role, with a focus on good pharmaceutical outcomes.
- Become the go-to professionals for optimising the use of medicines, including upgraded Structured Medication Reviews and post-discharge reconciliation.
- Offer prompt and accurate diagnosis, risk stratification based upon genotype and the capacity for personalised treatments.
- Increase medicines safety right across the care pathway.
- Build on hospital touchpoints – preparing people going into hospital for elective care, give them a soft landing back into the community and reduce readmissions.
- Dramatically improve access to primary care.
With informed policy-making and sufficient public investment, NHS community pharmacy could during the remainder of the 2020s develop much further as a clinical care and safe medicines supply service, in ways that will cost effectively benefit patients, public and the NHS, the document states.
NPA Chair, Nick Kaye, said: “Building out from the existing portfolio of services, there are some major opportunities within this decade, encompassing prevention, medicines optimisation, long term medical conditions and urgent care.
“We are seeking to challenge orthodoxies that have limited the sector’s scope for too long. At the same time, these ideas are firmly planted in reality because our start-point is what our paymasters in the NHS want, not what we can dream up.
“Some of this is about redrawing the borders of pharmacy practice – for example applying pharmacogenomics to pharmacist prescribing.
“Other aspects are about re-imagining what is our domain as a sector; we are rightly based firmly in the community but our impact ought to be felt and formalised across the entire system, including hospitals. We need to be ‘in the community but out of the box’.
“We are confident that the large majority of NPA members – by their nature innovators – are open to the idea of ambitious, transformative change.”
While pushing the boundaries of clinical service development, the NPA says it is also clear that the safe supply of medicines should continue to be a foundation stone upon which other pharmacy-based support is built.
In a foreword to the document, Dr Claire Fuller, Chief Executive of the Surrey Heartlands Integrated Care System, praised the NPA for backing a “can-do agenda” for the sector. “This is the kind of thinking – based in an understanding of what commissioners need – that makes people like me sit up and take notice”, she said.
Making Changes, Meeting Needs lists the enablers that would need to be in place in order to turn these ambitions into reality. They include digital connectivity, a boost to workforce and a supportive national contractual framework (in May, the NPA published its ‘New Deal for Community Pharmacy in England’ which describes such a framework).
The NPA is inviting people to offer feedback on their report, please write to independentsvoice@npa.co.uk.












