Rethinking cancer care: a system strategy for improved outcomes
Boosting early detection and reducing backlogs through data-backed, collaborative initiatives will be crucial to addressing the deteriorating state of cancer care in the UK, write Edge Health’s Lucia De Santis and George Batchelor.
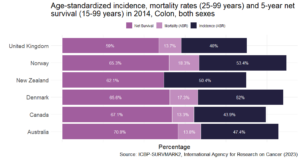
In the battle against cancer, the UK is grappling with alarming statistics, with outcomes for colon, lung and pancreatic cancers being particularly sobering. According to the Comparator report on cancer in Europe 2019, the UK was last out of all Western European nations for 5-year survival of colon cancer, as well as among International Cancer Benchmarking Partnership (ICBP) jurisdiction countries (Figure 1).
The complex factors behind the UK’s cancer outcomes
Understanding the root of this crisis is not straightforward, as many intertwined factors play roles, from cultural attitudes affecting help-seeking behaviours to underinvestment in critical medical resources. As a doctor in a busy acute trust, I could not grasp why one of my patients only presented to hospital long after his skin tone had turned an unmistakable dark shade of yellow, a tale-telling sign of his late-stage lymphoma. On the other hand, as of 2021, the NHS operated with around 63 decade-old LINACs (essential cancer treatment machines), and the UK has the lowest number of PET-CT scanners per 100,000 people among International Cancer Benchmarking Partnership countries.
The UK’s uphill struggle is deep-seated, with it having the worst cancer survival rates in the EU as far back as 1995. NHS’s low spending on cancer treatments and restricted access to cancer medicines for patients have been contributing factors.
Turning the tide: a dual-pronged strategy
Despite the complexity, there are attainable starting points for improvements: boosting early detection through the two-week-wait (2WW) referral pathway and ensuring prompt diagnosis and treatment through collaborative approaches that have proven successful in other countries.
Front one: boosting early detection
Data shows that cancers identified via a 2WW referral are often diagnosed earlier, and result in fewer diagnoses during emergency admissions, with implications for survival.
Analysis on stage at diagnosis performed by Cancer Research UK (Figure 2) demonstrates this clearly, with 30 per cent of cancers detected via 2WW referral being at Stage 1, versus just 8 per cent of cancers detected through an emergency presentation to hospital.
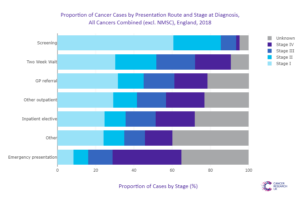
However, across England, there is a glaring disparity in cancer detection rates – that is, the number of confirmed cancers that are detected via an urgent suspected cancer referral (2WW). This is intimately related to the overall volume of 2WW referrals (Figure 3), where higher figures are associated with a higher detection rate.
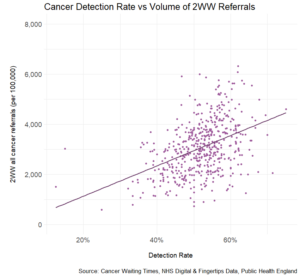
Patients whose practices have a lower threshold to refer under the 2WW programme fare much higher chances to have cancer detected via this route and as shown above, at an earlier stage. This, again, has implications for treatment and survival.
The national disparity between these practices not only means that average figures for cancer outcomes are affected by differing primary care strategies, but also that there are wide inequalities of care across the nation.
Cancer alliances and primary care networks can play an essential role in encouraging practices to revisit their referral behaviours. This effort can help reduce healthcare inequalities and potentially save lives by identifying and treating cancer earlier. Understanding what drives referral rates and promoting effective referral practices can make the difference between a life saved and one lost, and in the end spare the much higher healthcare and societal costs associated with late-stage cancer.
Front two: tackling backlogs through collaboration
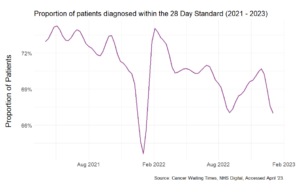
Our second strategy is to reduce backlogs through collaboration. The NHS’s diagnostic capacity is currently strained, as the steady decline in patients diagnosed within the 28-Day target since its 2021 introduction suggests.
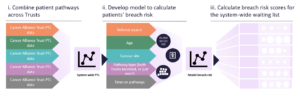
Taking cues from countries like Denmark, which successfully improved cancer survival rates by centralising specialised care and launching data-focused initiatives, the NHS can rethink its approach. By making comprehensive cancer patient data centrally available, we can make more informed decisions, improve workflow, and direct finances more effectively.
The NHS collects extensive data on cancer patients, encompassing their entire journey from referral to treatment. The key to better cancer care is ensuring the data is available centrally to key organisations and decision-makers, such as integrated care systems and Cancer Alliance leaders, to make evidence-backed financial, workflow and population health decisions and foster collaboration.
Sharing cancer data can help speed up diagnosis and treatment for patients. For instance, by sharing a cancer patient tracking list (PTL) across multiple trusts, patients who are at risk of breaching targets can be identified early and receive timely care. This strategy can also address the shortage of diagnostic appliances or services and specialised treatment.
The road ahead: data-driven initiatives and collaboration
The current state of cancer care in the UK calls for an urgent, systemic response. By prioritising early detection and fostering data-driven collaboration, we can significantly enhance the prognosis for the UK’s cancer patients.
Expediting early detection efforts, particularly through increased 2WW referrals, is crucial to change the narrative. These efforts, when paired with the power of collaborative and data-driven care models, can revolutionise the cancer care landscape. It’s a potent combination that can help us ensure that no matter where patients live, they can access timely and high-quality cancer care. This system-wide approach presents an opportunity not just to catch up with our European neighbours, but to potentially lead the world in effective cancer care.