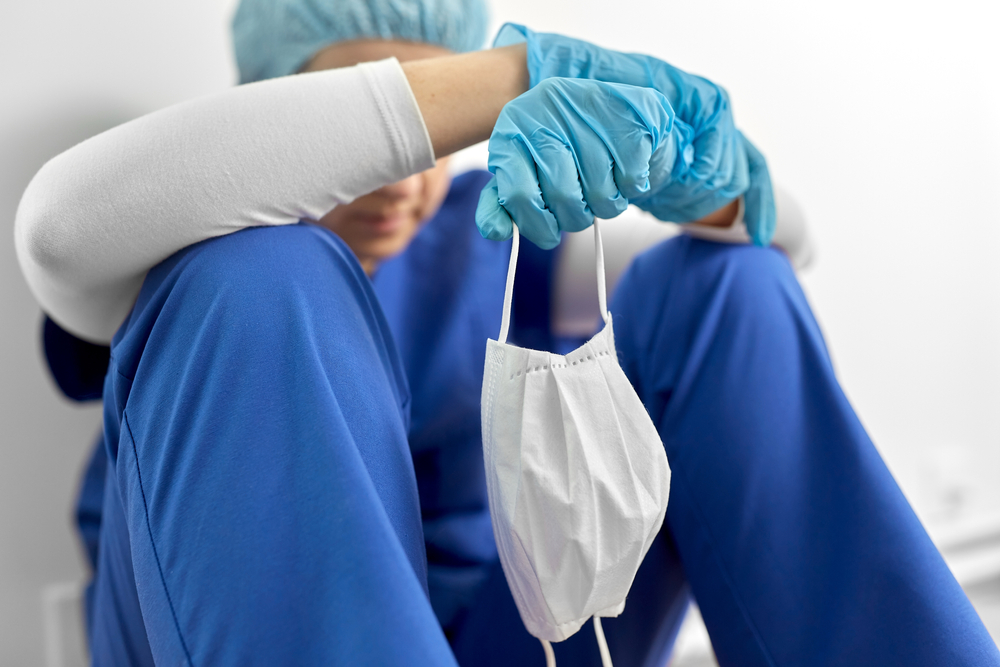
Despite challenges facing the service, the NHS remains one of the UK’s most loved institutions, says survey data, as NHS Charities Together launches new campaign urging public to continue supporting NHS and its staff.
More than three quarters (76 per cent) of NHS staff surveyed said they have experienced a mental health condition in the last year, according to new data collected by NHS Charities Together. Conducted by YouGov on behalf of the charity, the survey of more than 1000* NHS professionals also found that 52 per cent reported experiencing anxiety and 51 per cent reported struggling with low mood.
More than two-fifths of respondents (42 per cent) said they had experienced exhaustion in the last year, while three in five (60 per cent) reported feeling concerned for the mental health of colleagues.
Despite these challenges, however, 79 per cent of respondents said they feel proud to work for the NHS and 68 per cent said that they are unlikely to leave within the next 12 months.
The survey reveals the impact of increasing pressure on NHS staff, who are now subject to ‘winter pressures’ throughout the year, and are increasingly facing high workloads, long and unsociable hours and exposure to traumatic, stressful events. 96 per cent of those surveyed said they believe that overall pressure on NHS services is growing, and 69 per cent said that morale is the lowest they have ever experienced. A similar number (70 per cent) said that work-related stress has negatively impacted their mental health in the last year.
The release of these findings comes alongside the launch of a new campaign from NHS Charities Together called Support Goes Both Ways, which aims to raise awareness of need to continue to support NHS staff, so that they can best support the public.
Commenting on the findings, Ellie Orton OBE, CEO of NHS Charities Together, said: “Staff working within the NHS do a hugely challenging job every day, often dealing with traumatic events most of us would never encounter. The majority of NHS staff love doing the job they do, and both NHS staff and the general public feel proud of our NHS. But the nature of the work can have a detrimental impact on their mental health, and stigma can prevent them talking about it.
“Many NHS Trusts are already doing what they can to prioritise the mental health and wellbeing of our NHS staff, but it doesn’t go far enough. We will continue to work closely with NHS England and across the UK to ensure the additional support we provide for NHS staff has the most impact.”
In a separate survey, also carried out by YouGov on behalf of NHS Charities Together, more than 2,000 members of the public were invited to give their opinion on the NHS. Despite the challenges facing the NHS, the 2024 survey revealed that almost four in five (78 per cent) agreed that the NHS is one of the UK’s most loved institutions, compared to three in five (60 per cent) of the 2,000 respondents surveyed in 2022 who stated that the NHS is the best thing about the UK.
The proportion of respondents saying that they would consider a role working for the NHS if they were starting their career again, has risen slightly, from just over one in four (28 per cent) in 2021 to three in 10 (30 per cent) in 2024**.
Author, comedian and former doctor, Adam Kay, whose number-one bestselling book and multi-BAFTA-winning TV show, This is Going to Hurt, provided an insight into the often funny but harrowing daily life of a junior doctor, said: “These figures sadly come as no surprise at all. I know from my own experience just how hard NHS staff work, day-in, day-out, and the mental toll that routinely takes. We are uniquely privileged to have the NHS and should be proud of the wonderful people who sacrifice so much and go so far beyond the call of duty to look after us when we need it. But they desperately need support too, which is why I’m very proud to get behind NHS Charities Together’s Support Goes Both Ways campaign.”
Pat Chambers, Charity Development Manager, County Durham and Darlington NHS Trust Charity, said: “During the pandemic, many staff were affected mentally and emotionally. The extra support from NHS Charities Together enabled us to fund wellbeing spaces, equipment and food and drink for staff, who were working exhausting shifts in the constraints of PPE.
“We also received funding for the Trauma Risk Management (TRiM) project. TRiM is a trauma-focused peer support system helping to prevent extreme trauma and PTSD – similar to interventions delivered for service personnel returning from conflict zones. Funding enabled us to recruit 53 staff volunteers to be trained in providing peer support and interventions. We also funded a staff choir, which was a great outlet for staff and even saw us recording a single during lockdown, which hugely boosted morale.
“The unique challenges of the job means many NHS staff still face mental health challenges today, and the extra support is still needed, allowing us to promote wellbeing across our workforce and therefore ultimately continue to support the delivery of safe, compassionate and quality patient care.”
Hannah Canning is the Health and Wellbeing Coordinator at North West Anglia NHS Foundation Trust. Her role is fully funded by NHS Charities Together, through the North West Anglia Hospitals’ Charity, and was created to support frontline workers in the hospital. She said: “Thanks to the funding from NHS Charities Together, I’m able to support the wellbeing and mental health of staff in the hospital. I’m focusing on individual and team wellbeing and encouraging breaks and rest – considering all things that affect staff while they are on shift. Using this funding, we are able to go ‘over and above’ to support our staff.”
Ellie Orton OBE, CEO of NHS Charities Together, added: “NHS Charities Together already funds extra support such as counselling, green spaces, helplines and wellbeing zones and we’re launching Our Support Goes Both Ways campaign to raise awareness that while those who work for the NHS have a duty to care and protect us all, we all have a responsibility to make sure those who work for the NHS are looked after too.”
Steph Gorman is an intensive care nurse at Guys and St Thomas’s Hospital in London. She said: “I’m passionate about my work as a nurse. It’s hard, and I’ve had my struggles, but despite everything, it’s still one of the best jobs in the world. In the past, I’ve needed to seek help and started one-to-one counselling sessions at the hospital, which was really beneficial.
“Working as a nurse is still incredibly challenging. It’s so vital that we continue to invest in NHS staff mental health. NHS Charities Together have funded wellbeing zones at the hospital, just one example of the types of measures that really help make a difference.”
*Healthcare Professional sample: Total sample size was 1078 NHS staff. Fieldwork was undertaken between 13th – 19th February 2024. The survey was carried out online. The figures have been weighted and are representative of all NHS staff by occupational group.
**GB/UK Omnibus: Total sample size was 2068 adults. Fieldwork was undertaken between 16th – 18th February 2024. In 2022, total sample size was 2132 adults. Fieldwork was undertaken between 13th – 14th January 2022. For the 2021 survey, total sample size was 2120 adults and fieldwork was undertaken between 11th – 12th March 2021. The surveys were carried out online. The figures have been weighted and are representative of all UK adults (aged 18+) while for the 2022 survey, the figures are representative of all GB adults (aged 18+).